Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of global trade, China commodity inspection stands out as a critical mechanism ensuring quality and safety in imported and exported goods. As one of the world's largest economies, China's import and export activities are vast, impacting markets worldwide. Understanding the ins and outs of commodity inspection is essential for businesses navigating this complex environment.
Importance of China Commodity Inspection
China commodity inspection plays a pivotal role in maintaining standards that protect consumers and businesses alike. By enforcing regulations on product quality, safety, and compliance with international standards, inspections help to prevent subpar goods from entering or leaving the country. This process not only safeguards public health but also enhances China's reputation as a reliable trading partner on the global stage.
Overview of China's Import and Export Landscape
China's import and export landscape is characterized by its immense scale and diversity of products traded internationally. From electronics to textiles, what commodity was produced in China varies widely, showcasing the country's manufacturing prowess. The dynamics of trade are influenced by various factors including economic policies, consumer demand, and international relations.
Key Legal Frameworks Governing Inspections
The legal frameworks governing inspections in China are intricate yet essential for ensuring compliance with national standards. The Import and Export Commodity Inspection Law serves as a cornerstone for regulating how products are inspected before they reach consumers or enter foreign markets. Understanding these laws is crucial for businesses seeking to navigate the complexities of what is commodity inspection? while ensuring they meet all necessary compliance requirements.
What is Commodity Inspection?

Commodity inspection is a crucial process that ensures the quality and safety of goods exchanged in international trade. It serves as a gatekeeper, verifying that products meet specific standards before they enter or leave China’s borders. This practice not only protects consumers but also upholds the integrity of China's import and export landscape.
Definition and Purpose of Commodity Inspection
At its core, commodity inspection refers to the examination and evaluation of goods to determine their compliance with established standards. This can include checking for quality, safety, and adherence to legal regulations—essentially answering the question: What is commodity inspection? The purpose is multifaceted: it safeguards public health, protects the environment, enhances consumer confidence, and promotes fair trade practices.
In China, commodity inspection plays a pivotal role in maintaining the country's reputation as a global trading powerhouse. By ensuring that products are thoroughly inspected before reaching consumers or markets abroad, it helps mitigate risks associated with substandard goods. Thus, this process is integral not just for regulatory compliance but also for fostering trust between trading partners.
Historical Context of Inspection Practices
The roots of commodity inspection in China can be traced back centuries when merchants would assess goods for quality before sale. However, modern practices began taking shape in response to globalization and increased trade volumes in the late 20th century. As China's economy expanded rapidly, so did the need for more structured oversight—leading to enhanced regulations around what commodities were produced in China.
Historically, inspections were often inconsistent and varied by region or product type; this inconsistency posed challenges both domestically and internationally. Recognizing these issues prompted reforms aimed at standardizing practices across the nation to ensure compliance with international norms. Today’s robust framework reflects lessons learned from past inadequacies while addressing current market demands effectively.
Role of the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine
The General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (AQSIQ) stands at the forefront of enforcing commodity inspections in China. This government agency oversees various aspects related to product quality control—including import/export regulations tied directly to the Import and Export Commodity Inspection Law. Their mandate encompasses everything from agricultural products to manufactured goods ensuring that all comply with national standards.
AQSIQ's responsibilities extend beyond mere inspections; they also provide guidance on compliance requirements for businesses engaged in trade within China’s borders. By facilitating smooth operations through clear legal frameworks surrounding what does China export the most? AQSIQ plays an essential role in promoting fair competition while safeguarding public interests against unsafe or inferior products entering or exiting the country.
Moreover, AQSIQ's influence stretches into international markets where Chinese exports are scrutinized based on their adherence to safety protocols established by foreign governments—highlighting its significance not just locally but globally as well! Overall, understanding AQSIQ's function sheds light on how effectively China manages its commodity inspection processes amid evolving trade dynamics.
The Commodity Tax in China

Navigating the intricate web of commodity taxes in China is essential for anyone involved in international trade. The structure of these taxes can significantly influence the dynamics of import and export activities, impacting both compliance and profitability. Understanding the commodity tax in China not only helps businesses align with regulations but also enhances their competitive edge.
Understanding the Commodity Tax Structure
The commodity tax structure in China is multifaceted, designed to regulate various goods entering and leaving the country. It encompasses a range of duties that can vary based on product type, origin, and even market demand. For instance, certain commodities produced in China may attract lower tax rates to promote export growth while ensuring that imported goods are subjected to higher tariffs to protect local industries.
Taxation on commodities includes value-added tax (VAT), consumption tax, and import tariffs, each playing a distinct role in shaping trade practices. Businesses need to familiarize themselves with these components to effectively manage costs associated with china commodity inspection processes. Ultimately, a clear grasp of this structure enables companies to make informed decisions about pricing strategies and market entry.
How Commodity Taxes Affect Trade
Commodity taxes wield considerable influence over trade dynamics within China's bustling economy. High taxation on imports can deter foreign products from entering the market, thereby providing an advantage for domestically produced goods—what commodity was produced in China often gets prioritized under such conditions. Conversely, favorable tax rates for exports encourage manufacturers to push their products onto global markets.
As businesses strategize around these taxes, they must consider how fluctuations might impact their supply chains and pricing models. Additionally, understanding how changes in commodity tax policy could affect what does China export the most becomes crucial for long-term planning and adaptation strategies within competitive industries. In essence, navigating these waters requires a keen eye on both current regulations and potential shifts.
Compliance and Reporting Obligations
Compliance with china commodity inspection laws is non-negotiable for businesses operating within or exporting from China’s borders. Companies must maintain accurate records of their transactions related to commodities subject to taxation; failure to do so could result in penalties or disruptions during inspections—a critical aspect of what is commodity inspection? This means establishing robust reporting systems that ensure transparency throughout all phases of trade.
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies surrounding commodity taxes is vital for any entity involved in China's import-export ecosystem—especially considering its direct correlation with china commodity inspection processes as well as broader economic implications globally.
Key Commodities Produced in China
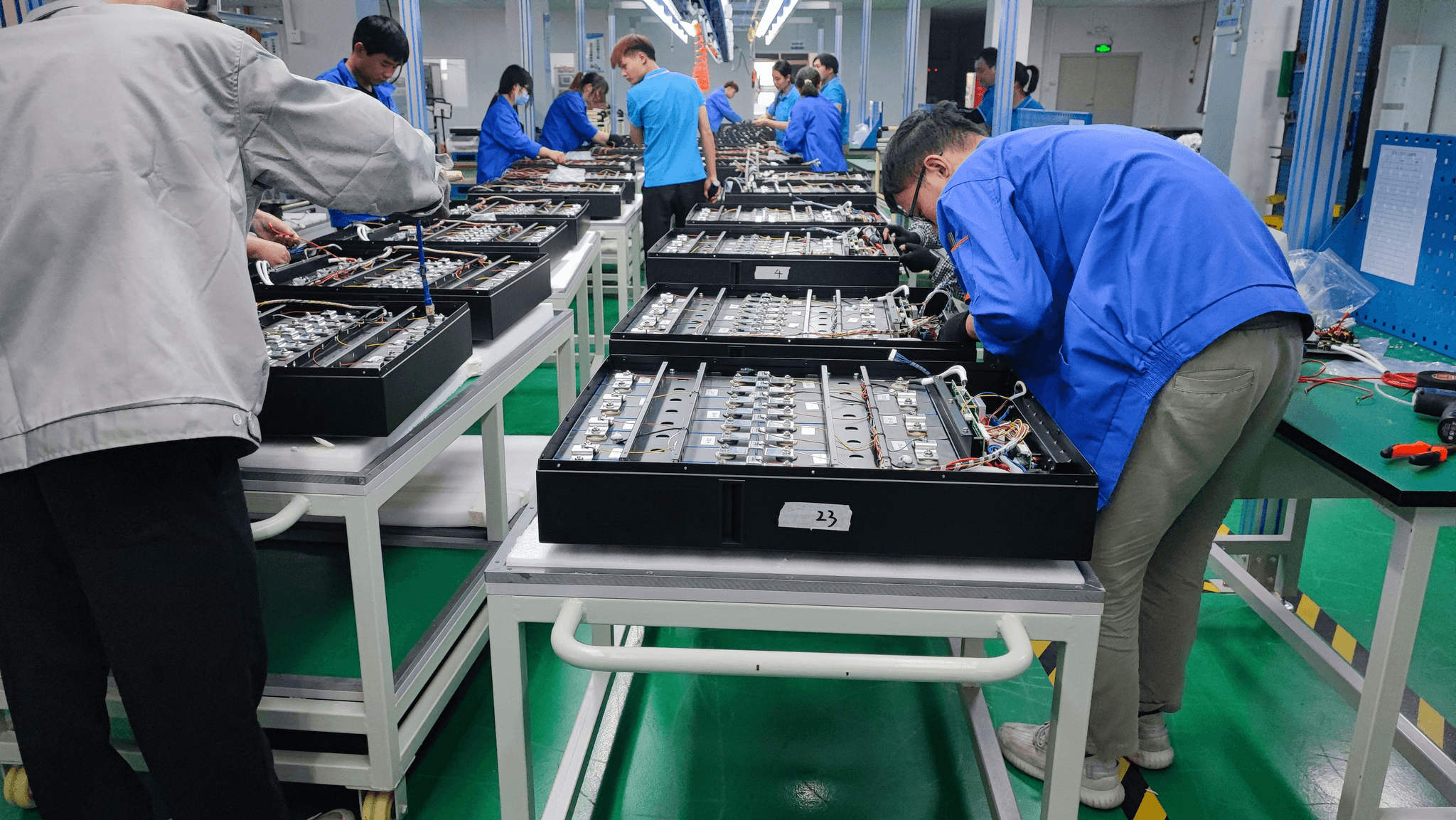
China is often referred to as the world's factory, and for good reason. The country is a powerhouse in the production of a wide array of commodities, which play a crucial role in both domestic and international markets. Understanding these key commodities not only sheds light on China's economic landscape but also highlights the significance of china commodity inspection in maintaining quality standards.
Overview of Major Export Commodities
When discussing what commodity was produced in China, one cannot overlook electronics, textiles, machinery, and agricultural products. Electronics, particularly smartphones and computers, dominate the export sector, contributing significantly to China's GDP. Textiles follow closely behind, with garments being shipped worldwide—an area where effective commodity inspection ensures that products meet international safety and quality standards.
Machinery exports are another vital component of China's trade portfolio; this includes everything from construction equipment to automotive parts. Agricultural products like rice and tea are also significant players in the export arena. As these commodities flow across borders, understanding what does China export the most becomes essential for businesses engaged in import and export commodity inspection law compliance.
Impact of Production on Global Markets
The sheer volume of commodities produced in China has a ripple effect on global markets; when China sneezes, many countries catch a cold! The influence extends beyond mere supply; it shapes pricing strategies across various sectors due to China's ability to produce goods at scale and often at lower costs. This has led to increased competition for manufacturers worldwide while elevating the importance of china commodity inspection as a means to ensure product integrity.
Moreover, fluctuations in Chinese production can lead to significant price changes globally—think about how shifts in textile production can affect fashion industries around the world or how machinery exports can impact construction projects elsewhere. Countries reliant on Chinese exports must navigate these dynamics carefully while adhering to import regulations that enforce compliance with established standards.
Trends in Commodity Production
As we look toward future trends in commodity production within China, sustainability is increasingly taking center stage. There’s a growing emphasis on environmentally friendly practices aimed at reducing waste and carbon footprints—an important consideration given global climate concerns. This shift not only aligns with consumer preferences but also impacts how china commodity inspection is conducted as more companies seek certifications that reflect their commitment to sustainability.
Technological advancements are also changing the landscape; automation and smart manufacturing are becoming commonplace within factories across China. These innovations enhance efficiency but also require robust systems for monitoring quality through effective inspections—a crucial aspect when considering what is commodity inspection?
In conclusion, understanding key commodities produced in China helps illuminate broader economic patterns while emphasizing the importance of compliance with both local laws and international standards regarding imports and exports.
What Does China Export the Most?
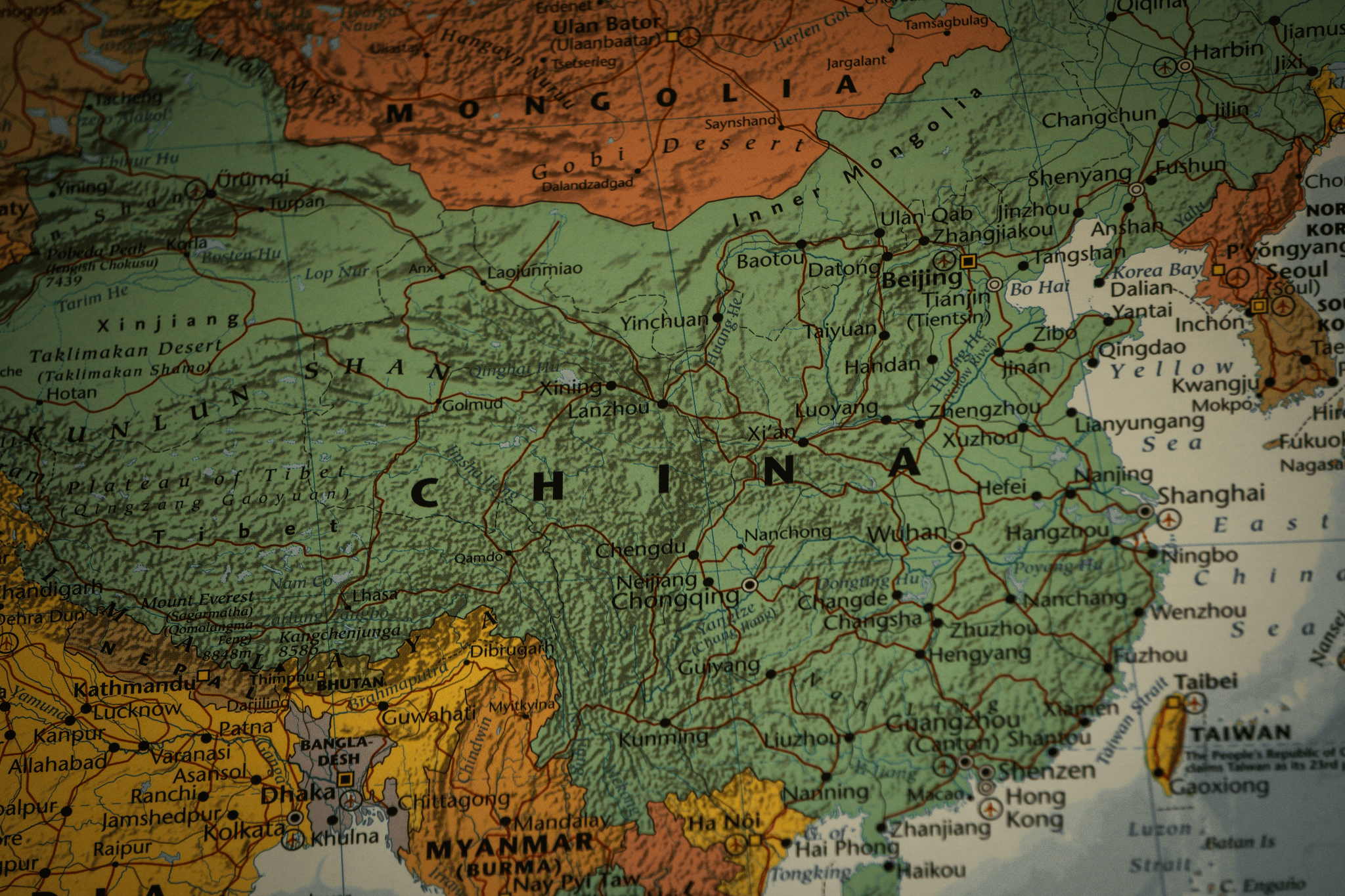
China's export landscape is a vibrant tapestry woven from various industries, reflecting its role as a global manufacturing powerhouse. The products that dominate China's exports are not just limited to traditional goods but also include high-tech items and consumer electronics. Understanding what China exports the most is essential for grasping the implications of commodity inspection and compliance with the Import and Export Commodity Inspection Law.
Analysis of Top Export Categories
When we delve into China's top export categories, electronics reign supreme, particularly smartphones and computers. Following closely are machinery, furniture, toys, and textiles—each contributing significantly to China's economy while navigating stringent china commodity inspection protocols. These categories highlight not only China's manufacturing capabilities but also its strategic focus on innovation and quality control.
The importance of understanding these categories cannot be overstated; they are subject to rigorous inspections under what is commodity inspection? regulations to ensure quality and safety standards are met before reaching international markets. As such, exporters must remain vigilant about compliance with both domestic regulations and international expectations.
Factors Influencing Export Growth
Several factors contribute to the robust growth of China's exports, including competitive pricing, technological advancements, and efficient supply chains. The interplay between these elements often leads to increased demand for Chinese products globally—an aspect that requires careful monitoring through effective china commodity inspection practices. Additionally, trade agreements with various countries have opened new doors for Chinese exporters by lowering tariffs and fostering smoother trade relations.
Another crucial factor is the rising middle class in developing nations that craves affordable consumer goods produced in China. This demographic shift drives demand for everything from electronics to textiles while placing pressure on manufacturers to comply with the What is the commodity tax in China? framework that governs financial obligations associated with exports.
Market Destinations for Chinese Exports
China's exports find their way into markets around the globe; however, key destinations include North America, Europe, and Southeast Asia. Each region presents unique challenges related to import regulations that necessitate thorough understanding of the Import and Export Commodity Inspection Law governing inspections in those areas. By aligning their practices with these legal frameworks, Chinese exporters can ensure seamless entry into diverse markets while adhering to necessary china commodity inspection standards.
Moreover, emerging markets in Africa and Latin America are becoming increasingly significant as they develop their infrastructure needs—often relying heavily on imports from China for machinery and construction materials. This expansion underscores the importance of knowing which commodities were produced in China as well as maintaining compliance with both local laws abroad and domestic regulations back home.
Import and Export Commodity Inspection Law

Navigating the intricate world of import and export commodity inspection law in China can feel like traversing a labyrinth. The legal frameworks governing these inspections are designed to ensure compliance, safety, and quality standards for commodities entering or leaving the country. Understanding these laws is essential for businesses looking to thrive in China's bustling trade environment.
Legal Framework Governing Inspections
The legal framework surrounding commodity inspections in China is multifaceted, encompassing various national regulations and international agreements. Central to this framework is the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (AQSIQ), which oversees the enforcement of inspection laws. These regulations detail what constitutes acceptable practices in commodity inspection, ensuring that products meet safety standards before they hit the market.
Moreover, the Import and Export Commodity Inspection Law serves as a cornerstone for understanding what is commodity inspection? It establishes procedures for inspecting goods at both ports of entry and exit, providing clarity on compliance requirements. This legal structure not only protects domestic consumers but also enhances global trade relations by maintaining high-quality standards for exports.
Role of AC&E in Compliance and Legal Guidance
When it comes to navigating the complex terrain of import and export regulations, companies often turn to organizations like AC&E (Advisory Council & Experts). AC&E plays a pivotal role in offering compliance advice related to china commodity inspection laws. They assist businesses by interpreting legal requirements, helping them understand what is required regarding inspections and certifications.
Additionally, AC&E provides resources that clarify what is the commodity tax in China? By offering insights into tax structures associated with imports and exports, they help businesses avoid pitfalls that could lead to costly fines or delays. Their expertise ensures that companies remain compliant while efficiently managing their supply chains within China's regulatory environment.
Consequences of Non-Compliance
Failure to adhere to china commodity inspection laws can lead to severe consequences for businesses engaged in international trade. Non-compliance may result in hefty fines, shipment delays, or even bans on exporting specific commodities altogether. Moreover, companies could face reputational damage if they are found distributing substandard products.
Understanding what does China export the most? can also shed light on potential risks; certain high-demand commodities attract more scrutiny during inspections due to their impact on public health or safety concerns. Therefore, staying informed about compliance obligations under import and export commodity inspection law is crucial for any business aiming for success in China's competitive market landscape.
Conclusion
As we wrap up our exploration of China commodity inspection, it’s clear that this process is not just a bureaucratic hurdle but a crucial component of international trade. Understanding what commodity inspection entails and its implications can significantly affect businesses engaged in import and export activities. With the right knowledge, companies can navigate the complexities of trade regulations and ensure compliance with the Import and Export Commodity Inspection Law.
Why You Should Care About Commodity Inspection
Commodity inspection is vital for maintaining quality standards in global trade, which ultimately affects consumer safety and market integrity. If you're involved in importing or exporting goods, understanding what commodity inspection is will help you avoid costly fines or shipment delays. Moreover, knowing how inspections work can give you a competitive edge by ensuring that your products meet all necessary requirements before they reach international markets.
Navigating the Legal Landscape in China
The legal landscape surrounding commodity inspections in China can be intricate, but it's essential for anyone looking to engage with Chinese markets. Familiarity with laws governing inspections allows businesses to comply effectively while also optimizing their supply chains. By understanding what the commodity tax in China entails and how it impacts trade, companies can better strategize their operations to avoid pitfalls associated with non-compliance.
Future Trends in China Commodity Inspection
Looking ahead, trends indicate that China's approach to commodity inspection will continue evolving alongside global trade dynamics. Innovations such as digital tracking systems could streamline processes while enhancing transparency and accountability within the supply chain. As global demand shifts and new commodities emerge from China, staying informed about what commodities are produced in China will be crucial for businesses aiming to capitalize on these changes.
